Nutritional Content of Cream of Wheat
Cream of wheat nutrition facts – Cream of Wheat, a popular breakfast cereal, offers a convenient and relatively quick way to start the day. Understanding its nutritional profile is key to making informed dietary choices. This section will detail the macronutrient and micronutrient composition of a typical serving, along with an examination of its glycemic impact.
Macronutrient Composition of Cream of Wheat
A standard serving of Cream of Wheat (typically 1/2 cup dry), prepared according to package directions, provides a significant amount of carbohydrates, a moderate amount of protein, and minimal fat. The exact values may vary slightly depending on the specific flavor and preparation method. However, a general breakdown is as follows: Carbohydrates comprise the majority of the calories, primarily in the form of complex carbohydrates.
Protein content is relatively low, contributing to a smaller portion of the overall calories. Fat content is negligible, making it a low-fat option. Fiber, an important component for digestive health, is also present in a moderate amount. For precise values, always refer to the nutrition label on the specific Cream of Wheat product you are using.
Vitamin and Mineral Content of Cream of Wheat
Cream of Wheat also contributes to daily micronutrient intake, though the amounts vary depending on fortification and preparation. The following table provides a general overview of the vitamins and minerals commonly found in a serving:
| Vitamin/Mineral | Amount per Serving (approx.) | % Daily Value (approx.) | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | 2-3 mg | 10-15% | Supports red blood cell production and oxygen transport. |
| Niacin (B3) | 2-4 mg | 10-20% | Contributes to energy metabolism and cell function. |
| Folic Acid (B9) | Variable, check label | Variable, check label | Essential for cell growth and development, particularly important during pregnancy. |
| Other B Vitamins (Thiamin, Riboflavin) | Small amounts | Small percentages | Support various metabolic processes. |
Note
The values provided are approximate and may vary based on the specific product and serving size. Always refer to the nutrition facts label for the most accurate information.*
Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load of Cream of Wheat
Cream of Wheat possesses a relatively high glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL). The GI measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood glucose levels, while the GL considers both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a serving. The high GI and GL of Cream of Wheat mean it can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, which can be a concern for individuals with diabetes or those managing their blood sugar.
This rapid rise is primarily due to its high carbohydrate content and the relatively quick digestion and absorption of these carbohydrates. For individuals concerned about blood sugar control, consuming Cream of Wheat in moderation, alongside protein and fiber-rich foods, may help mitigate this effect. For example, adding berries or nuts to your Cream of Wheat can help slow down the absorption of carbohydrates and reduce the overall glycemic impact.
Cream of Wheat Variations and Nutritional Differences

Cream of Wheat, while seemingly simple, offers a range of varieties, each with subtly different nutritional profiles. Understanding these variations allows for more informed choices based on individual dietary needs and preferences. This section will explore the nutritional differences between various Cream of Wheat products and the impact of adding common ingredients and adjusting preparation methods.
Nutritional Comparison of Cream of Wheat Varieties
Different Cream of Wheat varieties, such as the original, multigrain, and sometimes limited-edition flavors, contain varying amounts of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. These differences stem from the inclusion of additional grains and ingredients.
- Original Cream of Wheat: Primarily consists of refined wheat, offering a smoother texture but lower in fiber compared to other varieties. It’s a good source of carbohydrates for quick energy.
- Multigrain Cream of Wheat: Incorporates several grains, like oats, barley, and wheat. This results in a higher fiber content, contributing to improved digestion and satiety. It may also boast a slightly higher protein content compared to the original.
- Other Varieties: Specific nutritional values vary depending on the added ingredients. For example, a cinnamon-flavored variety might contain added sugar, impacting the overall sugar content. Always check the specific nutrition label for the most accurate information.
Impact of Added Ingredients on Nutritional Value
Adding ingredients like fruits, nuts, and sweeteners significantly alters the nutritional profile of Cream of Wheat. While enhancing flavor and texture, these additions can influence the overall caloric content, sugar levels, and micronutrient intake.
| Added Ingredient | Calories (Approximate) | Sugar (Approximate) | Fiber (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 cup Blueberries | 40-50 | 5-7g | 2g |
| 1/4 cup chopped Almonds | 180-200 | 1-2g | 3g |
| 1 tablespoon Honey | 60 | 17g | 0g |
*Note: These values are estimates and can vary depending on the specific brand and type of ingredient used.*
Effect of Preparation Methods on Nutritional Composition
While the fundamental nutritional content of Cream of Wheat remains relatively consistent, the cooking method can subtly influence its properties.The water ratio significantly impacts the final consistency and calorie density. A thicker Cream of Wheat, made with less water, will have a higher concentration of carbohydrates and other nutrients per serving. Conversely, a thinner consistency, made with more water, will result in a lower calorie density but potentially reduced nutrient concentration per serving.
Similarly, longer cooking times may lead to some nutrient loss, although the effect is usually minimal for this particular food.
Cream of Wheat in a Balanced Diet

Cream of Wheat, while a convenient and quick breakfast option, requires careful consideration within the context of a balanced diet. Its role depends heavily on how it’s incorporated into a broader eating plan that encompasses a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Understanding its nutritional profile is key to leveraging its benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks.Cream of Wheat can be a valuable part of a balanced diet when consumed mindfully.
Its primary nutritional contribution is carbohydrates, providing a source of readily available energy. This can be beneficial for individuals needing a quick energy boost, particularly athletes or those with physically demanding jobs. However, its relatively low micronutrient density—meaning it lacks a significant amount of vitamins and minerals— necessitates careful consideration. Relying solely on Cream of Wheat for breakfast would create a nutritional deficit.
To counteract this, it’s crucial to pair it with foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients.
Dietary Concerns Related to Regular Cream of Wheat Consumption, Cream of wheat nutrition facts
Regular consumption of Cream of Wheat, without careful consideration of other dietary components, poses potential concerns. The high carbohydrate content can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with sufficient physical activity and a moderate overall calorie intake. Furthermore, the relatively low fiber content, compared to whole grains, may not support optimal digestive health. The lack of significant amounts of vitamins and minerals necessitates supplementation through other food choices.
For example, a diet consisting primarily of Cream of Wheat would be deficient in essential vitamins like Vitamin C and Vitamin D, as well as minerals such as iron and calcium.
Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Cream of Wheat
A balanced meal plan incorporating Cream of Wheat should prioritize nutrient diversity. The following sample plan demonstrates how to integrate Cream of Wheat into a healthy and balanced daily diet. Portion sizes should be adjusted based on individual caloric needs and activity levels.
Cream of wheat, a breakfast staple, offers a decent source of fiber and iron, though its nutritional profile is relatively simple. For those seeking a richer source of protein and calcium, however, you might compare it to the nutritional powerhouse that is parmesan cheese nutrition facts , which provides a significant boost in those areas. Ultimately, both offer distinct nutritional benefits, depending on individual dietary needs and preferences.
Returning to cream of wheat, it’s important to note its low fat content.
- Breakfast: 1/2 cup Cream of Wheat cooked with water or unsweetened almond milk, topped with 1/4 cup berries (for antioxidants and fiber) and a sprinkle of chopped nuts (for healthy fats and protein).
- Lunch: Large salad with mixed greens, grilled chicken breast (lean protein), avocado (healthy fats), and a variety of colorful vegetables (vitamins and minerals). A light vinaigrette dressing.
- Dinner: Baked salmon (omega-3 fatty acids and protein), 1/2 cup brown rice (fiber and complex carbohydrates), and a side of steamed broccoli (vitamin C and fiber).
- Snacks: A piece of fruit (apple, banana, orange), a handful of almonds, or a small Greek yogurt (protein and calcium).
Cream of Wheat and Specific Dietary Needs: Cream Of Wheat Nutrition Facts
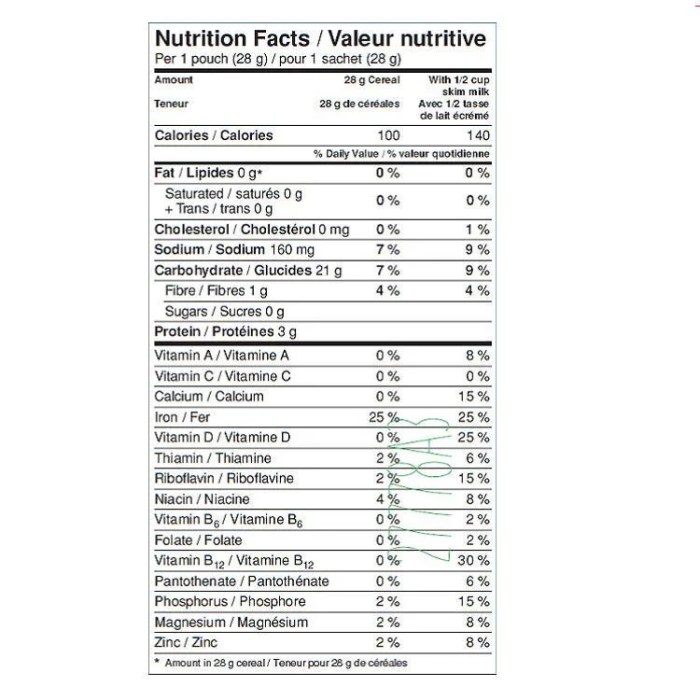
Cream of Wheat’s suitability as a breakfast option depends heavily on individual dietary needs and restrictions. Its simple ingredient list makes it a potentially good choice for some, but limitations exist for others. This section will explore Cream of Wheat’s appropriateness for various dietary needs and compare it to other breakfast cereals.
Cream of Wheat and Diabetes
Cream of Wheat, particularly the plain varieties, generally has a lower glycemic index (GI) compared to many other breakfast cereals. A lower GI means it causes a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar levels after consumption. However, the addition of sugar, honey, or fruit significantly increases the GI. Individuals with diabetes should carefully monitor their blood sugar levels after consuming Cream of Wheat and consider portion size, as well as added ingredients.
They might also benefit from choosing a plain variety and adding their own low-GI toppings, such as berries or a sprinkle of nuts.
Cream of Wheat and Gluten Sensitivity/Celiac Disease
Traditional Cream of Wheat is made from wheat, and therefore contains gluten. This makes it unsuitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. However, many brands now offer gluten-free Cream of Wheat alternatives, usually made from other grains like rice or corn. These gluten-free options provide a similar creamy texture and can be a suitable breakfast choice for those avoiding gluten.
Always check the product label carefully to confirm the absence of gluten.
Cream of Wheat and Allergies
Cream of Wheat’s primary ingredient is wheat, making it a potential allergen for individuals with wheat allergies. Cross-contamination during processing is also a concern. Those with wheat allergies must strictly avoid Cream of Wheat. Individuals with other allergies should carefully review the ingredient list for any potential allergens, such as dairy (in some flavored varieties). Gluten-free versions may contain other potential allergens depending on the substitute grain used.
Comparison of Cream of Wheat to Other Breakfast Cereals
The nutritional value and suitability of Cream of Wheat vary significantly compared to other breakfast cereals. The following table presents a comparison, highlighting key differences:
| Cereal | Gluten-Free Options | Fiber Content (per serving) | Sugar Content (per serving) | Suitable for Diabetes | Suitable for Gluten Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cream of Wheat (Regular) | No | Variable, depending on preparation | Low (plain), Variable (flavored) | Moderately suitable (plain) | No |
| Cream of Wheat (Gluten-Free) | Yes | Variable, depending on grain used | Low (plain), Variable (flavored) | Moderately suitable (plain) | Yes |
| Oatmeal | Yes (certified gluten-free oats) | High | Variable | Moderately suitable | Yes (with certified gluten-free oats) |
| Corn Flakes | Yes | Low | High | Less suitable | Yes |
| Bran Flakes | Yes (some brands) | High | Variable | Moderately suitable | Yes (some brands) |
Note: Fiber and sugar content can vary significantly depending on the specific brand and preparation method. Always check the nutrition label.
Cream of Wheat and Weight Management
Cream of Wheat’s role in weight management is complex. Plain Cream of Wheat is relatively low in calories and fat, making it a potentially suitable option for weight loss when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. However, adding sugar, butter, or other high-calorie ingredients can significantly increase its caloric content, negating its potential weight-management benefits.
The high carbohydrate content can also lead to blood sugar spikes if not managed properly. For weight management, individuals should opt for plain Cream of Wheat and focus on incorporating it into a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Portion control is crucial.
User Queries
Is Cream of Wheat a good source of protein?
No, Cream of Wheat is relatively low in protein compared to other breakfast options. It’s primarily a carbohydrate source.
Does Cream of Wheat contain gluten?
Regular Cream of Wheat contains gluten. However, gluten-free varieties are available.
Can I add Cream of Wheat to smoothies?
Yes, cooked Cream of Wheat can be blended into smoothies to add thickness and creaminess, enhancing nutritional value if you add fruits, vegetables, or protein powder.
How long does cooked Cream of Wheat last in the refrigerator?
Cooked Cream of Wheat should be refrigerated and consumed within 3-4 days for optimal freshness and safety.
Is Cream of Wheat suitable for weight loss diets?
It can be, but portion control is crucial due to its carbohydrate content. Combining it with protein and healthy fats can help manage satiety and prevent blood sugar spikes.








0